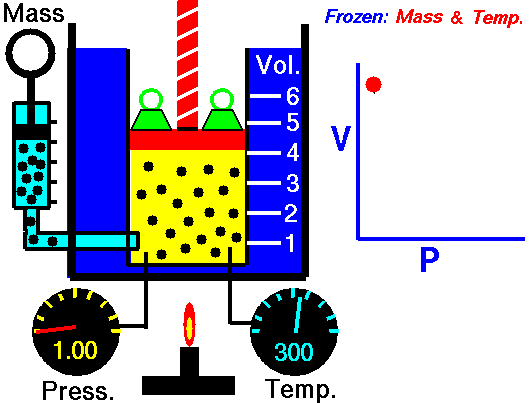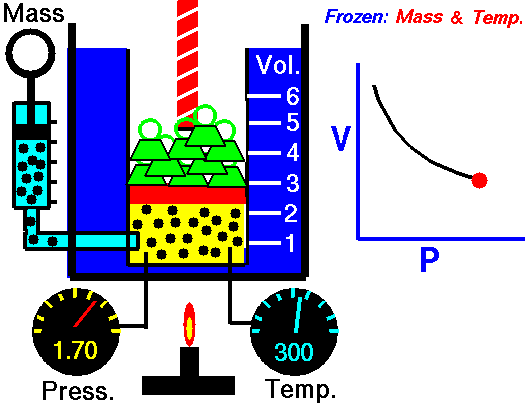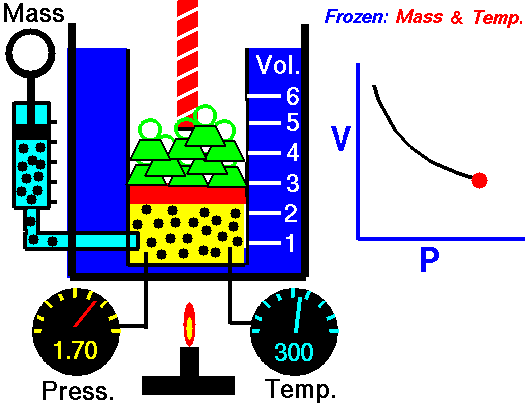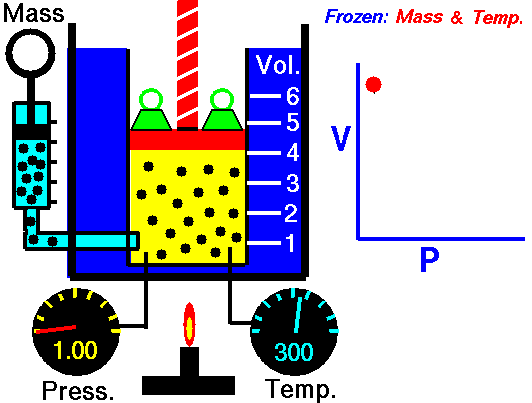
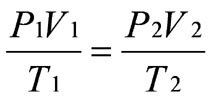The volume of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature, but is inversely proportion to the pressure. Since the Combined Gas Law is a combination of both Boyle's Law and Charles' Law, you can refer back to previous animations to further understand.
Boyle's Law
Charles' Law
The formula for the Combined Gas Law is:
In the formula...
P1 = The original pressure of the gas
V1 = The original volume of the gas
T1 = The original temperature of the gas
P2 = The new pressure of the gas
V2 = The new volume of the gas
T2 = The new temperature of the gas
The formula can only be used if you know five out of the six values. For example, if you had the original volume, temperature, and pressure of the gas, and you have two of the three new values, you could use the Combined Gas Law formula.
When using the formulas for the gas laws...
- STP (or Standard Temperature and Pressure) is often used
- Standard temperature is 273 K (always use Kelvin when using gas law formulas)
- Standard pressure is 1 atmosphere (or 101.3 kPa, 760 Torr, 760 mmHg, 14.7 psi)
- kPa = Pascal (Pa) S.I. Unit
- mmHg = millimeters of Mercury
- psi = Pounds per square inch
Practice with the Combined Gas Law...
If you have 4.0 liters of gas at STP, and you want to know the volume of the gas at 2.0 atm of pressure and 30 degrees Celsius, the following steps must be taken:
1. Identify the original pressure, or P1. The problem gives us standard temperature and pressure. Due to this, we know that P1 = 1 atm.
2. Identify the original temperature, or T1. The problem gives us STP. Due to this, we know that T1 = 273K.
3. Identify the original volume, or V1. The problem provides us with 4.0 Liters of gas. Due to this, we know that V1 = 4.0 Liters. Since the new volume, or V2, is the variable we need to solve for, our answer is going to be in Liters because the original volume is in Liters.
4. Identify the new pressure, or P2. The problem provides us with 2.0 atm of pressure. Due to this, we know that P2 = 2.0 atm of pressure.
5. Identify the new temperature, or T2. The problem provides us with 30 degrees celsius. Since temperature must always be in Kelvin, we need to know how to convert from Celsius to Kelvin.
QUICK LESSON
Kelvin = Degrees in Celsius + 273
Celsius = Kelvin - 273
6. Using the formula "Kelvin = Degrees in Celsius +273," we can calculate our new temperature by adding 273 to 30. Once we have done this, we know that T2 = 303K.
7. Identify the new volume, or V2. V2 is not provided and, due to this, we know that V2 is our unknown variable.
8. Using our known values, plug them into the formula: P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2
9. (1.0)(4.0)/273 = (2.0)(V2)/303
(V2)(2)(273) = (1)(4)(303)
(546)(V2) = 1212
V2 = 2.2
The new volume, or V2, is 2.2 Liters.
For more practice with the Combined Gas Law formula, please visit this website:
http://science.widener.edu/svb/tutorial/combinedgascsn7.html
For a more in depth explanation of the gas laws, please visit this Youtube video:
www.youtube.com/watch?v=CGq5s9_-2A8